Morgan Chopper
Q. How Morgan Chopper does work?
Q. Morgan Chopper working, waveforms & applications in power electronics
Q. Why do we use a saturated reactor in a Morgan’s chopper?
Circuit diagram of Morgan Chopper :
- Figure A shows the circuit diagram of the Morgan chopper. SCR T1 is the main thyristor.
- D ,C and the sable reactor (SR) together form a forced commutation circuit to turn off SCR D1. The diode FWD is a freewheeling diode.
- The Morgan chopper makes use of a Saturable Reactor (SR) which is a Saturable reactor (SR) which is a type of inductor. When SR is Saturated, it has a very low inductance.
- When it is not Saturated, it has a very high inductance.
- Assume that the commutating capacitor C is initially charged with its left side positive with respect to right side plate,i.e. Vc = + Vs.
Operation of Morgan Chopper :
- Refer figure A for waveforms to understand the operation.
 |
| Figure A |
Mode 1 :
- Figure B and C show the equivalent circuit in mode 1 of operation.
 |
| Figure B |
 |
| Figure C |
- T1is turned on at t = a. C now discharges via C – T1– SR – C1. But since SR is not saturated, its inductance is very high (almost open). Thus C continues to discharge very slowly and Vc is almost constant.
- As T1is ON, the load receives full supply Vs – Lf is a filter inductance and GWD is freewheeling diode. The load current flows via supply – T1 – Lf – Load-Supply.
- At a time t = b,due to the discharge of C into SR,it saturate and its impedance becomes very low. Therefore Vc will now reverse its polarity.
- But this polarity is not applied across T1 as SR now opposes to change current direction. It’s impedance again increase.
- Therefore eventhough Vc has charged to Vswith opposite polarity, still T1is off as SR reverts to high impedance state quickly.
Mode 2 :
- Now I begins to discharge via C-SR-D-C. SR has high impedance. Load current flows as said in Mode 1 above.
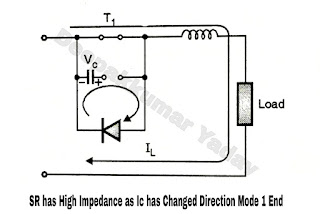 |
| Figure D |
- At t = C, due to the discharge current of capacitor C, The SR satuates and offers very low impedance. The voltage across Vc reverse biases T1and T1 is off.
- C now reverse to Vc = Vs polarity i.e. original polarity. The discharge of Ic via D now stops as Vc reverses. SR becomes off as Ic discharge is zero. This is the initial condition. Cycle repeats from Mode 1 onwards.
 |
| Figure E |
Why saturable reactor?
- Instead of a Linear Reactor a Saturable Reactor has been used in Morgan chopper. The time required for LSR and C to complete saturation i.e. TONis fixed. Thus the average output voltage can be changed only by changing frequency.
- If a dc current is passed through saturable core, TON can be varied (as in case of magnetic amplifiers).
- Due to this there is a saving in cost.
Type of commutation :
- Morgan chopper makes use of current commutation. It is a class B type commutation.
