Improved Series Inverter [Type 2]
Circuit diagram of Improved Series Inverter :
- Figure A shows the circuit diagram of the improved series inverter (type 2).
- In the basic series inverter circuit, the power delivered to the load was taken from the DC source in only one half cycle (in +ve half cycle).
- In the – ve half cycle the load power was taken from the commutating capacitor C1. (See Figure C).
- Thus for the basic inverter circuit the dc supply as to supply an intermittent current.
- Due to the intermittent flow of power from the dc supply, the dc supply needs to have a large peak current rating and the input current has high harmonic contents.
Improved Series Inverter
- This drawback can be eliminated by rearranging the series inverter circuit as shown in Figure A. In this circuit the power is drawn from the input dc supply in both the half cycles of output waveform.
 |
| Figure A |
 |
| Figure B |
Operation of Improved Series Inverter :
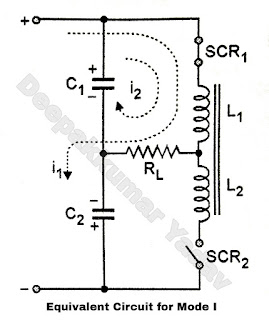
- Let the initial voltage on C2 be ec, and voltage across C1, be (V + ec) with the polarities shown in Figure A.
- When SCR1, is turned on at instant t0 the load current will be sum of two currents i1, and i2 as shown in Figure B.
- i1, is the charging current for C2, whereas iz is discharge current of C1.
- The current i1, is taken from the dc supply.
- The driving voltage (V + ec), the circuit elements and the initial conditions are identical for both these paths. Therefore i1, and i2 will be equal in magnitude.
- At the end of one half cycle when load current becomes zero SCR1 is turmed off due to natural commutation and voltage across C1, and C2, will be reversed.
[VC1 = -ec and
- Identical operation takes place in the – ve half cycle from t2, when t3, is turned on.
- In this half cycle one half of load current will be supplied from the input dc supply and other half from the discharging capacitor C2 as shown in Figure C.
- However as the load voltage waveform is dependent on the load, the series inverter finds very little practical applications.
- The inverter configurations in which the load voltage is independent of the load are practically preferred. They are Parallel inverter and Bridge inverter.
 |
| Figure D |
Applications of Series Inverter :
Some of the applications of the series inverter are :
- In the induction heating.
- In the ultrasonic equipments.
- To provide supply the cycoconverters.
Advantages of Series Inverter :
- Commutation circuit is simple.
- It is possible to increase output frequency beyond the resonant frequency of the LC circuit with the modified series inverter circuit.
- It is possible to obtain a sine wave output by making TOff zero


Sir inverter ma dc input diya jata ha to negative half cycle ka matlab kya ha