Classification of Wind Mills
The wind mills can be classified as follows :
Based on orientation of the axis of rotor
(a) Horizontal axis
(b) Vertical axis
Based on type of rotor
- Propeller type (Horizontal axis)
- Multiple blade type (Horizontal axis)
- Savonius type (Vertical axis)
- Darrieus type (Vertical axis)
1. Horizontal Axis Wind Mills :
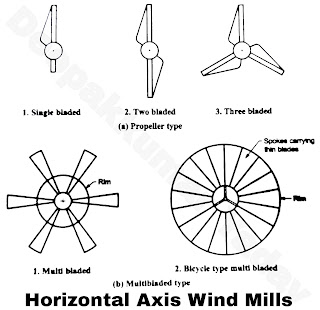 |
| Figure A |
- Horizontal axis wind mills may be propeller type or multibladed type as shown in Figure A. The orientations of the axis of their rotors are kept along the horizontal axis which can be adjusted so that it is parallel to the direction of wind stream.
- Most commonly used wind mills are propeller type with two or three blades for economical reasons. Though the two blade designs are more cost effective but it faces the difficulty of vibrations during orientation to wind direction called yaw control. However, these have been built today for large units in the capacity of 2 MW to 3 MW due to the availability of suitable materials now and the suitable controls and teetering.
- Three blades designs are otherwise preferable since its rotor is naturally balanced. These are used for power generation in low capacity of 15 kW upto higher capacity of 3 MW.
- Blades of propeller type wind turbines are made of aerofoil section. The mills are mounted on the top of the tower. The rotational speeds of propeller type are in the range of 300-400 rpm while the speeds of multiblade type wind mills are 60 to 80 rpm.
- The material used for blades is glass fibre reinforced plastic. Multiblade rotor consists of number of curved sheet metal blades with increasing chord length away from the centre. Number of blades used are 12 to 20 which having their inner and outer ends fixed on to the respective rims. Diameter of rotors used generally varies from 2 m to 5 m.
2. Vertical Axis Wind Mills :
- Vertical axis wind mills use the blades either Savonius type or Darrieus type as shown in Figure B.
- In order to fabricate a Savonlus rotor, a hollow elliptical cylinder is sliced into two pieces and each of these halves fixed to a vertical axis with a fixed gap. It forms S-shape due to this savonius type rotors are also called as S-rotors.
- Darrieus type rotors consists of two or three convex blades with aerofoil cross-section. Along their length the blades are curved into a shape called troposkein. The blades are mounted symmetrically on a vertical shaft. The advantage of vertical wind mills is that no orientation of vanes of the mill is required according to the direction of wind. These wind mills can generate power with the wind coming from any direction. It has low cut-in speed as low as 8 kmph while for propeller type turbine has the cut-in speed of 16 kmph for their effective operation. Another advantage is that these wind mills do not require very tall structures to support the mill. Only requirement is that these mills are installed at locations where there is a free flow of air.

