Industrial End User (Electrical Distribution System)
- At the industrial end user premises, again the plant network elements like transformers at receiving sub-station, switchgear, lines and cables, load break switches, capacitors, cause losses, which affect the input-received energy. However the losses in such systems are meager and unavoidable.
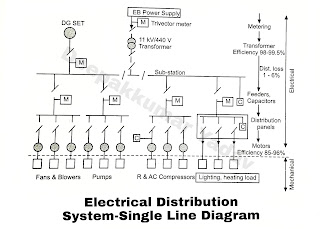
- A typical plant (single line diagram) of electrical distribution system is shown in Figure.
- After power generation at the plant it is transmitted and distributed over a wide network. The standard technical losses are around 17%, in India.
- But the figures for many of the states show transmission and distribution losses ranging from 17-50%. All these may not constitute technical losses, since unmetered and pilferage are also accounted in this loss.
- When the power reaches the industry, it meets the transformer.
- The energy efficiency of the transformer is generally very high. Next, it goes to the motor through internal plant distribution network.
- A typical distribution network efficiency including transformer is 95%, and motor efficiency is about 90%. Another 30% is lost in the mechanical system, which includes, coupling, drive train, a driven equipment such as pump and flow control valves, throttling etc. Thus, overall efficiency becomes 50%.
- Hence, one unit saved in the end user is equivalent to two units generated in the power plant.