LASERS :
Construction and Working of LASER :
Construction and Working of LASER :
- Laser means “Light Amplification by Simulated Emission of Radiation”.
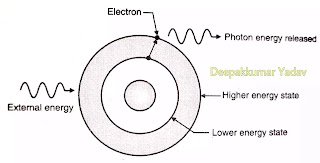
- Consider an atom when external energy (electromagnetic) is applied to it electron jumps from lower energy state to higher energy state.
- This electron emits electromagnetic radiation and light The colour of the light depends on frequency and wavelength.
- The energy released is known as photon energy. This process is called absorption. After a short time, the electron again goes to previous lower energy state emitting photon in the process.
- This is known as spontaneous emission. If a photon passes near to this electron, it causes the electron to decay.
- This causes emission of photon. Both photons are in the same phase. The above action described is fundamental for laser action.
- Under desired conditions, if atom undergoes stimulated emission, the atoms releases more photons. The action is cumulative and a chain reaction is formed which releases lot of photons.
- A large amount of energy is released. The wavelength of all photons is same. This process is known as amplification by simulated radiation.
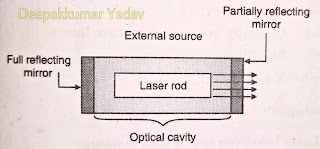
- figure shows arrangement for production laser light energy.
- It consists of external source in the form of flashing light source, two mirrors, laser rod.
- The full reflecting mirror has high reflecting capacity (about 99 %). The other mirror has less reflectivity.
- External source is in the form of flashing light. When light flashes on laser rod, stimulated emission takes place. The photons travel back and forth due to mirrors.
- The amplification takes place. When energy released is greater than certain limit , laser light comes out in the form of sharp beam. The laser beam comes out from partially reflecting mirror.
- The laser beam intensity depends on-size of laser rod, optical cavity, location reflectivity of mirrors.
There are many Types of LASER. These and below :
- Gas lasers
- Liquid lasers
- Chemical lasers
- Optically pumped solid state lasers
- Semiconductor lasers
- X – ray lasers.
Advantages of LASER :
- Laser beam can travel long distance.
- Can be used for beautification.
- Can be used in medical equipment.
- Can be used in metal processing industries.
Disadvantages of LASER :
- Operating equipment, control gear is required.
- Cost is more.
- High intensity may cause damage to organs.
- Strict safety precautions are necessary.
Applications of LASER :
- Special light effects required for media work.
- In metal works for cutting of metals, welding of metals.
- Medical field – Many surgical instruments are laser based.These are used in surgery.
- Laser beam arrangement is used in CD drive of computer for reading/writing data on CD.
- In missile launchers and other defense applications.