Parallel Inverter (with Purely Resistive Load)
Circuit diagram of Parallel Inverter :
- Circuit diagram of a parallel inverter is as shown in Figure A.
- The parallel inverter is sometimes also called as the centre tapped inverter because this configuration needs a centre tapped transformer on the output side It is also called as a push pull inverter.
- The thyristors S1and S2 are switched alternately to connect the input dc source V in alternative senses across the two halves of the transformer primary.
- This induces a square wave voltage across the load in the transformer secondary.
- C is the commutation capacitor. The voltage on the capacitor is used to turn off a conducting SCR, by turning on the nonconducting SCR.
 |
| Figure A |
Operation of Parallel Inverter :
Mode I :
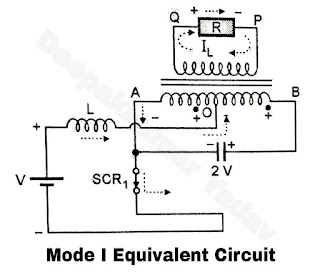
- When SCR1 is turned on the dc source voltage appear across the left half of the primary OA
- The primary current flows from O to A Due to the transformer action the voltage between AB is 2 V Volts
- Hence the capacitor is charged to a voltage of 2 V Volts. The load voltage is positive, so is the load current (Figure B).
 |
| Figure B |
- The firing of SCR2 turns off SCR1 by the principle of parallel capacitor commutation. (The capacitor voltage is applied across SCR1 directly to reverse bias it).
- The input dc voltage now gets connected across winding OB. The primary current flows form O to B, through SCR2 as shown in Figure C.
- The load voltage changes its polarity, and the direction of load current is reversed. Thus load voltage and current both become negative.
- The square output waveform is thus obtained across the load.

